On this page:
What is a renewable energy zone?
Renewable energy zones are areas identified as the best places to host wind and solar projects and batteries for storage.
In designing these areas we’ve considered community and industry feedback as well as information about cultural heritage, existing uses of land, and quality of wind and solar energy in the region.
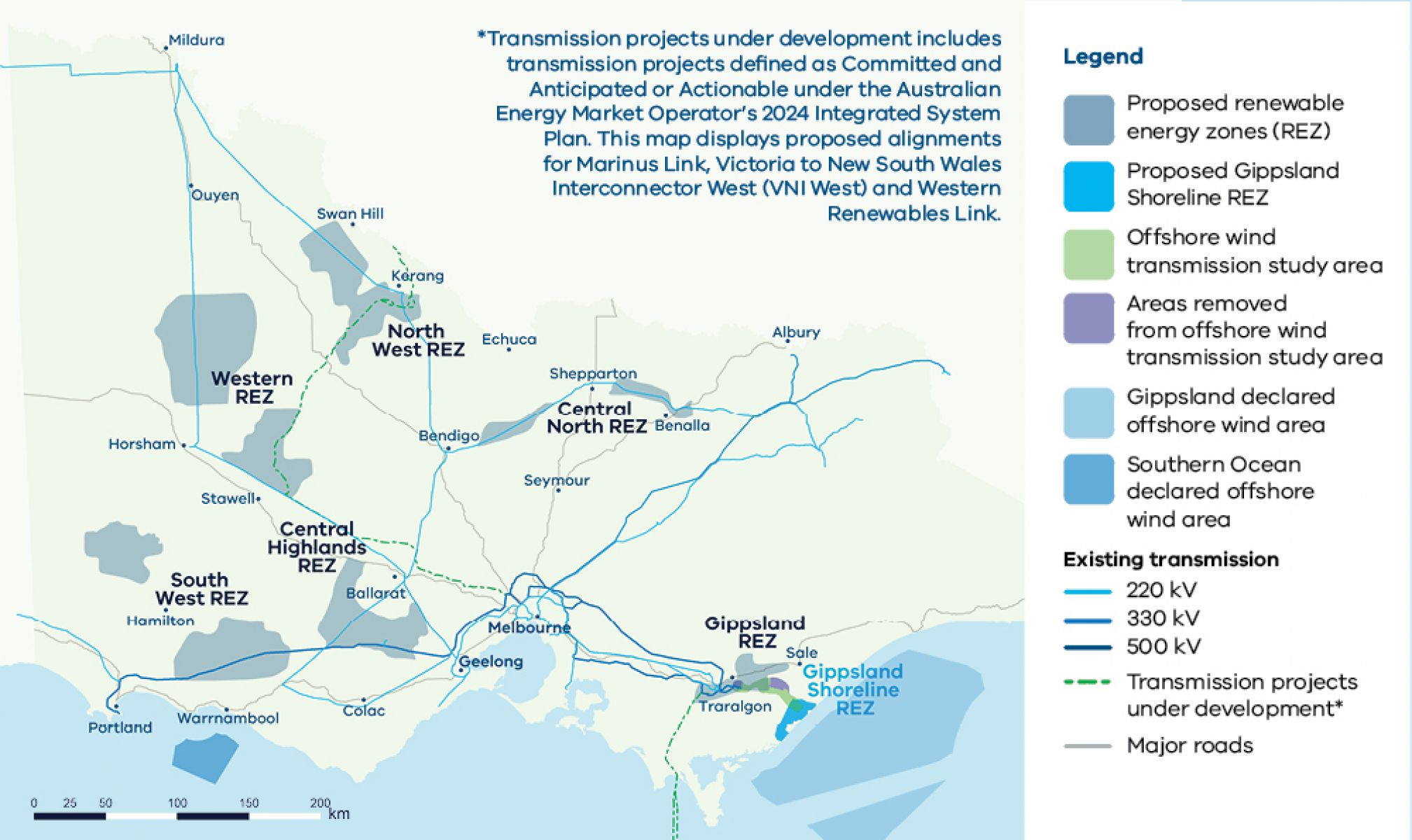
Victoria’s proposed renewable energy zones
The 2025 Victorian Transmission Plan has identified 6 proposed renewable energy zones.
It also includes a shoreline zone in Gippsland designed specifically to locate infrastructure such as underground cables that will connect offshore wind farms to the grid.
Click through to learn more about each zone:
- South West
- Central Highlands
- Western
- North West
- Central North
- Gippsland
- Gippsland Shoreline Renewable Energy Zone, for offshore wind connections
Interactive map
See the proposed renewable energy zones in more detail and download shape (GIS) files in our online interactive map.
How renewable energy zones were selected
Choosing areas for renewable energy zones involved carefully balancing many factors.
We considered:
- access to strong winds or sunshine that could produce renewable energy
- access to existing or planned transmission infrastructure
- if farming in the area could co-exist with renewable projects
- impacts on the environment and biodiversity
- impacts on local communities
- impacts on Traditional Owners and culturally sensitive areas
- interest from renewable energy project developers.
Not all community or industry requests have been adopted in the location of zones.
The Victorian Transmission Plan reflects difficult choices, made by weighing up these factors to deliver a plan that best serves all Victorians.
The benefits of renewable energy zones
Renewable energy zones will:
- unlock new economic benefits for regional communities and Traditional Owners
- limit the need for additional transmission infrastructure
- help set clear expectations for how project developers engage and involve the community
- provide greater certainty about how and where renewables projects should be built.
The Victorian Government is introducing a new approach to community benefits, set out in the draft Renewable Energy Zone Community Benefits Plan.
It includes new Renewable Energy Zone Community Energy Funds to benefit regional and rural communities, payments for landholders who host new transmission and guidance for payments for significantly impacted neighbours of new transmission.
The plan also outlines our commitment to work with Traditional Owners on a new approach to economic benefits.
For more information, visit Engage Victoria.
Next steps
The proposed renewable energy zones in the 2025 Victorian Transmission Plan will each go through a formal process to be declared a Renewable Energy Zone.
This process will include 6 weeks of public consultation, which will give landholders, communities and Traditional Owners another opportunity to provide feedback and shape decision-making.
Communities within proposed renewable energy zones can continue to provide feedback and seek more information about the zones, including through face-to-face meetings with VicGrid.
New grid access arrangements
As part of the declaration process, an access limit will be proposed for each zone. This will be a cap on the amount of different types of renewable projects – such as wind turbines and solar farms – that can apply to connect to the grid in the zone.
We are proposing to set access limits at the maximum amount that can be managed by the planned build-out of the transmission network.
This is not the level of development people should expect in each zone but is the maximum that the transmission network can support within the zone.
Once renewable energy zones are declared, VicGrid proposes to run a competitive allocation process to decide which projects in each zone have the authority to connect the energy they produce to the grid.
We will consider:
- the amount of electricity Victoria needs to generate to meet expected demand as outlined in the Victorian Transmission Plan
- ensuring the level of development inside each zone can be supported by available transmission lines
- the density of projects within each zone
- how development can be coordinated to avoid the ‘spaghetti effect’ of many powerlines crossing the landscape
- whether developers are meeting expectations for landholder, community and Traditional Owner engagement and benefits.
This will ensure we ultimately produce enough energy to meet demand while also considering the impact on communities, Traditional Owners, agriculture and the environment.
To find out more about how VicGrid is proposing to manage how projects gain access to connect to the grid, visit Engage Victoria.
Page last updated: 18/08/25
